What are the advantages of using a transdermal patch?
If you’ve seen advertisements for nicotine patches, you’ve already witnessed the ever-expanding popularity of adhesive patches and transdermal absorption. Yet, these small medical products have a far wider range of possibilities than you might expect.
As a flexible material converter, Strouse has helped design and manufacture several adhesive patches for transdermal absorption. By informing you about the manufacturing process in greater detail, we hope to prepare you so that your project runs more smoothly.
Over the years, it’s become clear that adhesive patches carry numerous advantages. By the end of reading these key benefits of adhesive patches, you should understand the perks of their absorption abilities.
Transdermal Patches in a Nutshell
What exactly are transdermal patches? As mentioned in the nicotine patch example above, transdermal patches are convenient for administering medication for a range of conditions. They stick to the skin and gradually release the drug in specific, pre-set doses through the skin rather than other, more traditional methods.
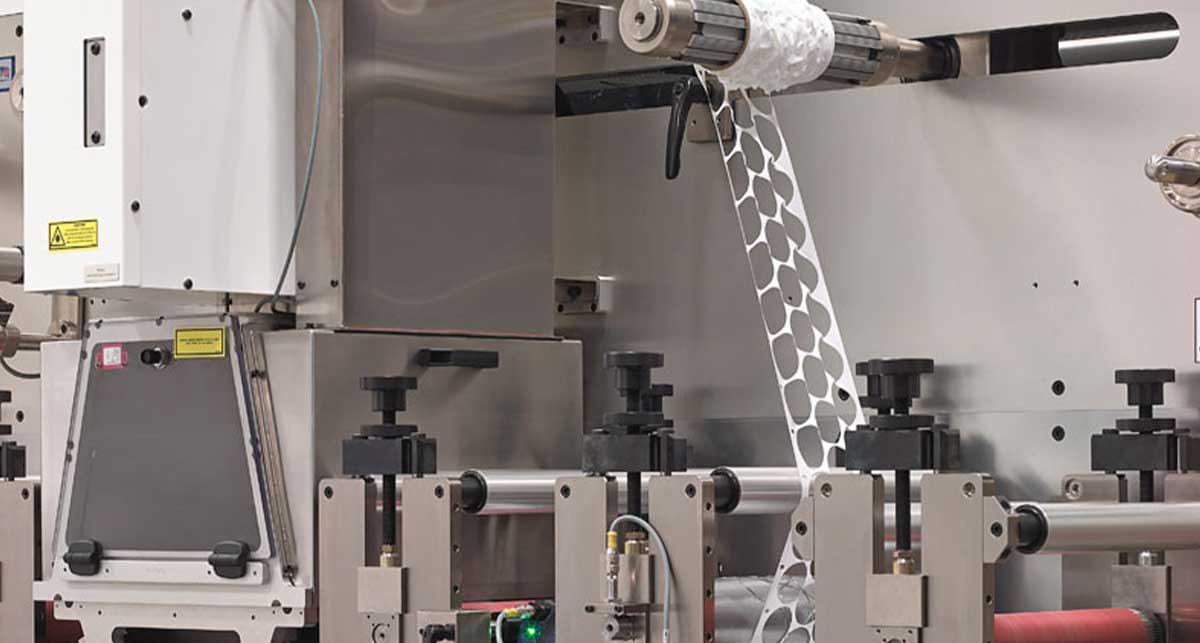
Adhesive transdermal patches are typically composed of several elements, including the backing, the drug reservoir, a membrane, and the adhesive that attaches to the skin. These design features are all designed to work together with the specific drug to release appropriate amounts over time. New advancements in this field have removed the need for the drug reservoir and mixed the medicine with the adhesive, making the transdermal patch more inconspicuous.
So, how is this method of medicating patients beneficial? Let’s go over some of the most significant advantages.
1. EASE-OF-USE
While we wouldn’t strictly advise anyone to “set it and forget it” when it comes to any health-related products, transdermal patches offer convenience in that a patient (or medical professional if needed) can place the patch on the skin and continue their day as normal.
Depending on the patch type (and assuming all goes according to plan), patients don’t need to stop what they’re doing as frequently to take a pill or worry about the invasive poke of a needle.
Similar to how peel-and-stick patches are attached, they can be removed easily — though not so easily that they fall off accidentally.
2. MEDICATION ADHERENCE
It’s not always easy for medical providers to get their patients to adhere to a medication schedule, let alone remember to take them. The ease of using adhesive patches makes it easier for patients to comply with their doctor’s orders and take their medicine as needed.
In addition to helping the person who needs this drug, it also helps maintain a good relationship between doctor and patient.
3. SMOOTHER DOSING
The transdermal absorption method delivers the medication smoothly, dosing the patient with the appropriate amount over an extended period. The smoothness of a continuous dose can make for better treatment than the uneven dosing that might occur when taking drugs orally.
Also, the consistency makes it easier to combat any adverse side effects. If an adhesive patch isn’t working or the patient experiences any negative side effects, they can peel it off to stop the medication from being administered. Due to the nature of how the drug is delivered, those side effects may go away sooner.
4. AVOIDING DIGESTIVE SIDE EFFECTS
While transdermal patches are not entirely without the risk of harmful side effects, one particular type of side effect can generally be avoided: digestive.
Oral drugs can cause digestive side effects, like nausea or upset stomach. Sometimes, this is precisely because the drug was taken by mouth and landed in the stomach. The transdermal patch delivers the drug to the bloodstream through the skin, avoiding a trip through the digestive tract and possibly any side effects that come with it.
5. ALTERNATIVE ADMINISTRATION TO NAUSEATED/UNCONSCIOUS PATIENTS
Transdermal patches aren’t just for easy take-home use for patients; they can also be used in moments of acute care, possibly in urgent situations. If a patient is unconscious and needs a drug in their system immediately, these patches are one way to administer it.
Similarly, suppose a patient is nauseated and can’t keep anything down. In that case, transdermal absorption can be an alternative delivery method to bypass their digestive system and get the drug they need into their bloodstream.
The Role of Adhesives in Transdermal Patches
When creating transdermal patches, it is essential to consider the type of skin adhesive used. The adhesive must stick to the skin without falling off when covered with clothing and be easy enough to remove without irritation.
Additionally, the adhesive must withstand other conditions, like sweat, heat, cold, and other environmental factors. All this while ensuring the drug can pass through to reach the patient.
Each type of transdermal patch functions differently and could have particular adhesive, backing, or liner requirements. If you’re at the point of working on your design, consider contacting a flexible material converter like Strouse for a better understanding of what the best method is for manufacturing your ideal component.
Adhesive Patches and Manufacturing
Working with skin adhesives is an inevitable part of designing any transdermal patch. Still, you may not have all the expertise when it comes to efficiently producing medical-safe adhesive patches on a machine press.
When manufacturing medical and skin-safe adhesive products, there are many rules and regulations, not to mention medical tape pricing factors which can make the whole process more lengthy and costly than other components.
Rather than wait to encounter a problem in the middle of production, reaching out to a converter early will help you plan for a fully optimized design and manufacturing phase.
Consider reaching out or looking further into our Learning Center for more information on adhesive patches and their production and development.
Originally published: Dec 2, 2021